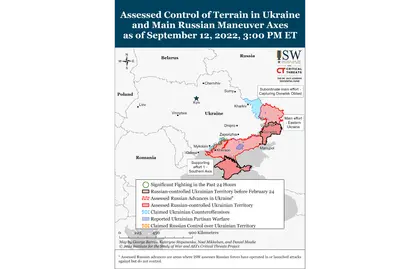
Key Takeaways
- Ukrainian forces are continuing to make impactful gains in Kherson Oblast and are steadily degrading the morale and combat capabilities of Russian forces in this area.
- The Russian military command may be suspending the deployment of newly formed units to Ukraine due to recent Russian losses and overall degraded morale.
- Russian forces are failing to reinforce the new frontline following Ukrainian gains in eastern Kharkiv Oblast and are actively fleeing the area or redeploying to other axes.
- Ukrainian forces continued targeting Russian military assets and positions in Kherson Oblast, likely steadily degrading them.
- The Ukrainian recapture of Izyum has likely degraded Russian forces’ ability to conduct artillery strikes along the Izyum-Slovyansk highway.
- The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) announced the restoration of the second reserve power transmission line to the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP).
- Ukraine’s sweeping counteroffensive is damaging Russian administrative capabilities and driving Russian departures from occupied parts of Ukraine far behind the line of contact.
Ukraine’s southern counteroffensive is continuing to have significant impacts on Russian morale and military capabilities in southern Ukraine. Satellite imagery of known Russian positions in Kyselivka, 15km northwest of Kherson City, shows that all but four Russian vehicles have departed from previous forward positions, consistent with rumors that Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) troops have abandoned Kyselivka and moved back towards the Dnipro River.[1] Kyselivka is an operationally significant location for Russian forces around Kherson City because it is the last major settlement along both the E58 highway and a railway line between current Ukrainian positions and Chornobaivka, the outermost part of Kherson City. The apparent withdrawal of Russian troops from this position may compromise the Russians’ ability to defend the northwestern outskirts of Kherson City and suggests that Russian troops in this area perceive an imminent threat to their positions. Spokesperson for Ukraine’s Southern Operational Command, Natalya Humenyuk, stated on September 12 that Russian forces located along the right bank of the Dnipro River in Kherson Oblast are attempting to negotiate for surrender under the auspices of international law.[2] Ukrainian operations in Kharkiv Oblast are unlikely to have had such a dramatic psychological effect on Russian troops this far south, and both the withdrawal of troops from forward positions in Kyselivka and reports of surrender negotiations are indicators that Ukrainian counteroffensives in the south are progressing in a significant way, even if visibility on this axis is limited by the shift in focus to Kharkiv.

Diane Francis Interviews Mikhail Zygar, Yaroslav Trofimov on Prospects of Russia’s War on Ukraine
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
The success of recent Ukrainian counteroffensive operations may be impacting the will or ability of the Russian military command to use newly formed volunteer units in Ukraine in a timely fashion. The Ukrainian General Staff reported that the Russian military command has suspended sending new, already-formed units to Ukraine due to recent Russian losses and widespread distrust of the Russian military command, factors which have caused a large number of volunteers to categorically refuse to participate in combat.[3] This assessment is still unconfirmed, but low morale due to Ukrainian counteroffensive success may prove devastating to the Kremlin’s already-poor ability to generate meaningful combat capability. The deployment of these newly formed units to reinforce defensive lines against Ukrainian counteroffensives would be an operationally-sound decision on the part of Russian military leadership; and the delay or potential suspension of these deployments will afford Ukrainian troops time to consolidate and then resume the offensive, should they choose to do so, without having to face newly arrived and fresh (albeit undertrained and understrength) units.
Authors: Karolina Hird, Grace Mappes, Katherine Lawlor, George Barros, and Frederick W. Kagan
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter