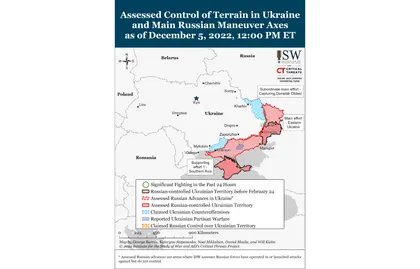
Key inflections in ongoing military operations on December 5:
- Russian forces continued to defend their positions along the Svatove-Kreminna line against Ukrainian attacks.[16]
- Russian forces continued to make incremental gains around Bakhmut but have not yet surrounded the city, and conducted offensive operations in the Avdiivka-Donetsk City area. Ukrainian sources claimed that small Russian assault groups of 15-20 personnel are attempting to penetrate Ukrainian lines.[17]
- Russian occupation officials continued the forceful transfer of Ukrainian children from occupied territories in Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts to Russia under the guise that the children require special medical care.[18]
- Russian forces shelled more than 20 settlements on the right (west) bank of the Dnipro River and continued to strike Kherson City.[19]
- Russian senator Andrey Klishas of the ruling United Russia party proposed the Kremlin restrict the ability of Russians who fled the country to avoid mobilization to secure work upon returning to Russia.[20]
- Ukraine’s Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) reported that the Russian military, in concert with the Russian Internal Ministry, is taking steps to launch an electronic database by February 2023 to document the personal details of all servicemen and restrict their movement even when out of uniform.[21]
Russian forces conducted another wave of missile strikes targeting Ukraine’s energy infrastructure on December 5. Russian and Ukrainian sources reported on December 5 that Russian forces conducted missile strikes targeting Ukrainian civilian and energy infrastructure in Kyiv, Odesa, Vinnetysia, and Zaporizhia Oblasts.[1] The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Ukrainian air defenses shot down 60 of over 70 missiles launched.[2] Deputy Head of Ukraine’s Presidential Office Kyrylo Tymoshenko Kyrylo Tymoshenko stated that the Russian strikes damaged a power supply line in Sumy Oblast.[3] ISW previously assessed on December 2 that while Ukrainian and Western-provided air defenses are further reducing Russia’s dwindling supply of precision munitions, the small percentage of Russian strikes getting through Ukraine’s air defenses are nevertheless having significant effects on Ukrainian critical infrastructure.[4]
- Check out the freshest Ukraine news items as of today.
- View the most recent Ukraine news pieces that came out today.
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
Ukrainian forces likely conducted strikes on two Russian strategic airbases on December 5, inflicting light damage while demonstrating Ukraine’s ability to strike Russian rear areas and possibly disrupt Russia’s campaign of strikes against Ukrainian infrastructure. The Russian Ministry of Defense and several milbloggers reported that Ukrainian forces used UAVs to strike the Engels-2 airbase in Saratov Oblast (approximately 315 miles from Ukrainian territory) and the Dyagilevo Air Base in Ryazan Oblast (approximately 285 miles from Ukrainian territory).[5] Both airbases house elements of Russia’s strategic bomber fleet, which Russia has employed to strike Ukraine throughout the war. Ukrainian Presidential Advisor Mikhail Podolyak tweeted that the Kremlin should have known that “if something is launched into other countries’ airspace, sooner or later unknown flying objects will return to departure point.” Still, Ukrainian authorities have not formally claimed responsibility for the strikes as of publication.[6] Russian sources claimed that a Ukrainian drone struck aircraft at the Engels-2 Airbase in Saratov Oblast, Russia, damaging strategic bombers and missile carriers.[7] Russian sources also claimed that a Ukrainian drone destroyed a Russian fuel truck at the Dyagilevo Air Base in Ryazan Oblast, Russia.[8] The Russian Ministry of Defense claimed that the strike intentionally targeted Russian long-range aircraft.[9] Ukrainian forces likely sought to disrupt Russian strikes against Ukrainian critical infrastructure and demonstrate Ukraine’s ability to target Russian strategic assets.

ISW Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, January 21, 2025
Anger over the Russian military’s inability to prevent the Ukrainian strikes on Russian strategic airbases over 280 miles from Ukrainian positions outweighed praise for the latest round of strikes against Ukraine within the Russian milblogger community. Russian milbloggers criticized Russian officials for failing to anticipate and prevent the drone strikes at the Engels-2 and Dyagilevo Air Bases on December 5.[10] Select milbloggers noted that Russian military officials have not adequately protected the airbases, with some suggesting that Russian officials did not adequately defend the bases despite knowing that they were clear targets for Ukrainian strikes.[11] Several prominent Russian milbloggers claimed that Ukrainian sabotage and reconnaissance groups must have launched the strike against the Engels-2 air base from inside Russian territory, asserting either that Ukrainian sabotage and reconnaissance groups are active inside Russia or – if the UAVs were launched from Ukrainian territory – that Moscow is under threat from Ukrainian territory.[12]
Russian milbloggers also called on Russian military officials to authorize significant retaliation strikes against Ukraine and intensify counter-terrorism measures within Russian territory.[13] The milblogger community complained that Russian military officials do not consider their suggestions and ignore open-source intelligence (OSINT) and that, had Russian officials taken milbloggers’ warnings into account, the two strikes on Russian military bases would have likely been prevented.[14] Select milbloggers suggested that the strikes on Engels-2 and Dyagilevo Air Bases threaten Russia’s legitimacy as a nuclear power as the strikes damaged aircraft capable of carrying multiple nuclear weapons.[15]
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter