Key Takeaways
- Russian government sources confirmed that Russian authorities are bringing Ukrainian children to Russia and having Russian families adopt them. The forcible transfer of children from one group to another “with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group” is a violation of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide.
- Russian authorities are deploying security forces to Luhansk Oblast likely in response to waning support for the war and growing unwillingness to fight among Luhansk residents. This deployment diverts these forces from operations elsewhere in Ukraine, likely contributing to the broader Russian failure to translate limited tactical gains into operational successes.
- Russian officials may have conducted a false flag event in Donetsk City to justify attacks against Ukrainian government buildings on Ukrainian Independence Day.
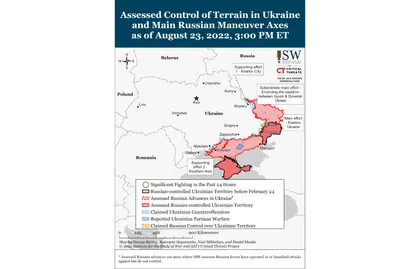
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast and south of Bakhmut, on the northwestern outskirts of Donetsk City, and southwest of Donetsk City.
- Russian forces made limited gains east of Mykolaiv City and in northwestern Kherson Oblast.
- Ukrainian forces continued to strike Russian military assets and ground lines of communication (GLOCs) in Kherson Oblast.
- Russian federal subjects (regions) are continuing to increase one-time enlistment bonuses for recruits, and are likely recruiting personnel with no prior military experience for specialist positions.
- Ukrainian partisan activity continues to disrupt Russian occupation activities.
Russian government sources confirmed that Russia is bringing Ukrainian children to Russia and having Russian families adopt them. Russian federal subject (region) Krasnodar Krai’s Family and Childhood Administration posted about a program under which Russian authorities transferred over 1,000 children from Mariupol to Tyumen, Irkutsk, Kemerov, and Altay Krai where Russian families have adopted them.[1] The Administration stated that over 300 children are still waiting to “meet their new families” and that citizens who decide to adopt these children will be provided with a one-time bonus by the state.[2] Ukraine’s Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) additionally reported that Russian officials transferred 30 Ukrainian children from Khartsyzk, Ilovaysk, and Zuhres in occupied Donetsk Oblast to Nizhny Novgorod under the guise of having the children participate in youth educational-training programs.[3] The forcible transfer of children of one group to another “with intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial or religious group“ is a violation of the Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide.[4]
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
Russian authorities are deploying security forces to Luhansk Oblast likely in response to waning support for the war and growing unwillingness to fight among Luhansk residents. The LNR Internal Ministry reported on August 23 that LNR Internal Ministry personnel conducted joint patrols with consolidated police detachments from the Internal Ministries of St. Petersburg and Leningrad Oblast in Starobilsk, Shchastya, and Stanystia, occupied Luhansk Oblast.[5] The LNR Internal Ministry also reported on August 22 that Rosgvardia (Russian national guard) units conducted security for Russian Flag Day celebrations in Starobilsk.[6] Ukraine‘s Main Intelligence Directorate (GUR) reported that Rosgvardia elements in Dovzhansk (formerly Sverdlovsk), Luhansk Oblast are not subordinate to the local LNR forces and that Rosgvardia conducted a search of an LNR official in Dovzhansk.[7] The deployment of Russian security forces to police-occupied areas of Luhansk Oblast supports ISW’s previous assessment that LNR residents and possibly militia forces may be unwilling to continue fighting now that they have reached the Luhansk Oblast borders.[8] Recent intensified Russian efforts to forcibly mobilize residents in Luhansk likely exacerbated this disillusionment, and Russian authorities may be increasing Russian security forces’ presence in Luhansk to suppress any internal instability and/or because they are losing confidence in indigenous Luhansk forces.[9]

Trump’s 90-Day Foreign Aid Freeze Won’t Apply to Ukraine Military Funding, Pentagon Assures VOA
Russian authorities’ deployment of Rosgvardia elements to security duties in occupied Luhansk Oblast diverts these forces from operations elsewhere in Ukraine, likely contributing to the broader Russian failure to translate limited tactical gains into operational successes. ISW previously assessed that Russian forces had likely exhausted their momentum from territorial gains around Avdiivka and Bakhmut, Donetsk Oblast – a very small section of the whole Ukrainian theater – partially due to their inability to allocate sufficient resources to offensive operations.[10] LNR forces’ unwillingness to fight in the war, coupled with Rosgvardia forces’ presence in the rear instead of near the front will likely contribute to continued Russian failures to make significant territorial gains.
Russian officials may have conducted a false flag event in Donetsk City on August 23 to justify attacks against Ukrainian government buildings on August 24, Ukrainian Independence Day. Social media networks in Donetsk City reported that a strike caused damage to the Donetsk People’s Republic (DNR) administrative building, where DNR Head Denis Pushilin works.[11] Pushilin was reportedly absent at the time of the strike. Russian media framed the attack as a direct Ukrainian strike on a DNR government building, potentially to set information conditions for retaliatory strikes against Ukrainian government buildings on Ukrainian Independence Day.[12] Ukrainian government authorities previously warned government workers in Kyiv to work from home the week of August 22 to 26 and cited concerns that Russian forces will target Ukrainian government assets as part of an extended missile and artillery campaign on Independence Day.[13] Russian-backed head of Kherson’s occupation administration Kirill Stremousov also claimed on August 22 that his administration was preparing for Ukrainian provocations on Independence Day, which could have been conditions-setting for a false-flag attack.[14]
Unverifiable sources reported that axis commanders in Ukraine are reporting directly to Russian President Vladimir Putin, bypassing both the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) and Chief of General Staff Valery Gerasimov in the chain of command. Independent Russian outlet Vazhnye Istorii or iStories quoted unnamed sources within the Russian General Staff stating that Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu has lost Putin’s trust after the initial phase of the full-scale invasion of Ukraine that failed despite Shoigu’s assurances of a swift victory.[15] The sources claimed that Putin now bypasses Shoigu and interacts directly with Commander of Central Military District Alexander Lapin who oversees the “central” group of forces in Ukraine, and the Commander of the Russian Aerospace Forces Sergey Surovikin who commands the “southern” group of forces. ISW cannot independently verify the validity of this report, but if the report is true, it indicates that Putin is also bypassing Gerasimov.
Authors: Karolina Hird, Kateryna Stepanenko, Grace Mappes, George Barros, and Frederick W. Kagan
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter