Key Takeaways
- The Kremlin’s heavy-handed approach to partial mobilization may successfully meet the Kremlin’s internal quota of mobilized personnel, but is unlikely to generate effective soldiers and is prompting significant domestic backlash for little gain.
- The Kremlin is openly not adhering to its promised conditions for partial mobilization.
- Kremlin quotas will likely force local officials to mobilize men regardless of their military status and will likely incentivize the mobilization of ethnically non-Russian and immigrant communities at a disproportionate rate.
- The Kremlin likely attempted to downplay a prisoner swap with Ukraine that is deeply unpopular among Russian nationalists and milbloggers by undertaking the swap the same day Putin announced partial mobilization.
- IAEA negotiations around the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant are unlikely to significantly improve the situation at the plant and may provide an opportunity for Russian forces to stage provocations.
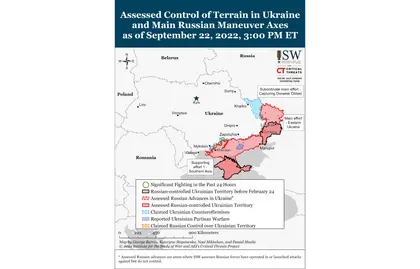
- Ukrainian forces likely continued limited counteroffensive operations along the Kharkiv-Luhansk Oblast border and continued attacks toward Lyman on September 22.
- Ukrainian military officials maintained their operational silence regarding Ukrainian ground attacks in Kherson Oblast on September 22 and reiterated that Ukrainian forces are conducting an operational-level interdiction campaign in Kherson Oblast.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks along the frontlines in Donetsk Oblast on September 22.
- Russian forces did not conduct any confirmed ground attacks west of Hulyaipole on September 22 and continued routine strikes throughout western Zaporizhia Oblast.
- Russian occupation forces are hurriedly setting conditions to hold sham annexation referenda across occupied Ukraine from September 23-27.
- Russian officials created polling stations in parts of Russia, ostensibly to enable displaced (in many cases meaning kidnapped) Ukrainian residents of occupied territories to “vote.”
- Russian occupation officials in Ukraine likely expect to be forced to provide personnel to meet Russian regional mobilization quotas after the Kremlin illegally annexes occupied Ukrainian territories.
The Kremlin’s heavy-handed approach to partial mobilization may successfully meet the Kremlin’s internal quota of mobilized personnel but is unlikely to generate effective soldiers and is prompting significant domestic backlash for little gain. Russian authorities are forcibly recruiting Russian citizens to fight in Ukraine on flimsy pretexts, violating the Kremlin’s promise to recruit only those with military experience. Russian authorities are also demonstrably mobilizing personnel (such as protesters) who will enter the war in Ukraine with abysmal morale. The Kremlin’s heavy-handed approach to partial mobilization will likely exacerbate domestic resentment of a measure that would have been unpopular even if implemented without the harsh approaches observed in the last 24 hours.
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
The Kremlin is openly not adhering to its promised conditions for partial mobilization just 24 hours after its September 21 declaration. Russian officials previously claimed that partial mobilization will only impact 300,000 men and only those with previous military experience.[1] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated on September 22 that the practice of administering mobilization notices to detained protesters does not contradict the September 21 mobilization law. Peskov’s threat contravenes the Kremlin’s claim that it will abstain from mobilizing men outside of composed reservist lists.[2] Western and Russian opposition media outlets reported instances of Russian military commissars administering draft notices to protesters in Moscow and Voronezh.[3] Russian opposition outlets also reported on a bank IT specialist who had received a draft notice despite never having served in the army or attended military-education courses in university.[4] The IT specialist is likely one of many Russian men who received mobilization notices despite not meeting the stated criteria for partial mobilization. A university student in Buryatia released footage of Rosgvardia and military police pulling students from lessons, reportedly for mobilization, despite Russian Defense Minister Sergey Shoigu repeatedly stating that Russian students will not be mobilized.[5]

Zelensky Meets CIA Director William Burns in Ukraine
Kremlin quotas will likely force local officials to mobilize men regardless of their military status. The quota for mobilized men remains unverifiable, with Kremlin officials claiming that Russia will mobilize only 300,000 men and Russian opposition outlets’ sources suggesting that the number might reach a million.[6] Regardless of the total quota, the Russian federal subjects executing the mobilization order will likely undertake recruitment measures outside of the outlined reservist call-up. Some Russian federal subjects such as the Republic of Yakutia (Sakha) and Kursk Oblast are imposing laws restricting reservists from leaving their places of permanent residence.[7] Russian enlistment officers and police are also reportedly enforcing unscrupulous mobilization practices (as ISW previously observed during their crypto-mobilization campaigns) by calling up men by phone, issuing notices in the middle of the night, and notifying men of their mobilization via state social benefits websites.[8]
The Kremlin will also likely mobilize ethnically non-Russian and immigrant communities at a disproportionate rate. A member of the Kremlin’s Russian Human Rights Council, Kirill Kabanov, proposed mandatory military service for Central Asian immigrants that have received Russian citizenship within the last ten years, threatening to confiscate their Russian citizenship if they do not mobilize.[9] Current Time reported that residents of Kurumkan, a village in the Republic of Buryatia, noted that Russian enlistment officers mobilized about 700 men of the total population of 5,500 people.[10] If witness reports from Kurumkan are accurate, they would indicate that Russian officials mobilized about 25% of the male population from a single village in a majority ethnically Buryat district. An Armenian Telegram channel published a mobilization list from Tuapse, Krasnodar Krai that reportedly consists of 90% ethnically Armenian residents, despite the town’s total Armenian community being only 8.5% of the population.[11]
The Kremlin’s heavy-handed approach to mobilization is prompting public anger and distrust across Russia. Independent Russian human rights outlet OVD-Info reported that protests took place in 42 cities across the country, including protests even in small villages in the Republic of Dagestan.[12] Unidentified assailants set fire to several military recruitment centers and local administration buildings in Nizhny Novgorod, St. Petersburg, Tolyatti, and Zabailkalsky Krai.[13] The Kremlin will likely subdue such protests in the coming days. However, the declaration of partial mobilization and blatant disregard for even the government-dictated parameters for the mobilization may alienate concerned swathes of the Russian public who were previously more tolerant of the less personally impactful Russian invasion of Ukraine.
The Kremlin likely attempted to downplay a prisoner swap with Ukraine that is deeply unpopular among Russian nationalists and milbloggers by undertaking the swap the same day Putin announced partial mobilization. The Kremlin exchanged 215 Ukrainian prisoners of war (POWs), including captured foreign nationals and Azov Battalion leaders, for at least 55 Russian POWs and political prisoners, including Putin’s personal friend, Ukrainian billionaire Viktor Medvechuk, on September 21.[14] The Russian Ministry of Defense claimed on September 22 that Russian and DNR and LNR POWs were in “mortal danger” in Ukrainian custody.[15] Far-right Russian milbloggers criticized the exchange and asked if the Kremlin had given up on the ”de-Nazification” of Ukraine, one of the stated goals of the Russian invasion.[16] Kremlin propagandists had heavily publicized the capture and planned prosecution of Azov personnel, accusing them of being Ukrainian Nazis. Other milbloggers criticized the Kremlin for enabling what they called Ukrainian information operations and ”allowing Kyiv to manipulate the mood in Russia.”[17] Chechen leader Ramzan Kadyrov described the exchange as ”incomprehensible,” implied that Chechen forces tortured Azov prisoners in captivity, and implied that Russian forces who capture ”Nazis” should kill them rather than take them as POWs if they will be traded back to Ukraine.[18] Torturing or killing POWs is a war crime and violates the Geneva Conventions.
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) announced that it began negotiations to establish a nuclear safety zone around the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP). Such negotiations are unlikely to significantly ameliorate the situation due to continued Russian efforts to stage provocations at the plant. IAEA Director General Rafael Grossi stated on September 22 that the IAEA had begun “productive conversations” with Ukrainian Foreign Minister Dmytro Kuleba, Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov, and French President Emmanuel Macron in order to establish a Nuclear Safety and Protection Zone at the ZNPP.[19] Despite the positive intentions of external negotiators, Russian forces may use negotiations as an opportunity to stage further provocations at the ZNPP and accuse Ukrainian troops of endangering the safety of the plant, as they have repeatedly done in the past. As ISW has previously reported, Russian forces previously exploited the IAEA presence at the ZNPP in order to accuse Ukraine of disregard for nuclear safety and blame Ukrainian forces for shelling the plant, despite being unable to provide visual evidence to support their accusations.[20] Russian authorities may seek to leverage the IAEA negotiations to accuse Ukraine of nuclear irresponsibility in an attempt to degrade continued Western support to Ukraine.
Authors: Karolina Hird, Kateryna Stepanenko, Katherine Lawlor, and Mason Clark
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter