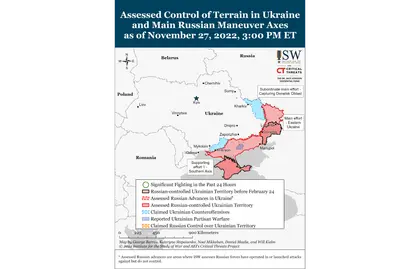
Key inflections in ongoing military operations on November 27:
- The Ukrainian General Staff reported that Russian officials are preparing for another wave of covert mobilization starting on December 10 in the Russian Federation and in Russian-occupied territories in Ukraine.[13]
- Russian milbloggers widely criticized the Russian Federal Customs Service for customs delays and exclusions of dual-use goods that volunteer movements have been sending to the Russian military.[14]
- The Ukrainian General Staff reported that the Russian forces along the Svatove-Kreminna line are conducting defensive operations around Kupyansk and offensive operations west of Kreminna.[15]
- Russian sources reported that Ukrainian troops continued counteroffensive operations toward Svatove and Kreminna.[16]
- Russian forces continued offensive operations around Avdiivka.[17] The Ukrainian General Staff did not report that Ukrainian forces repelled any ground attacks around Bakhmut on November 27, suggesting that Russian forces may have advanced in the area.[18]
- Russian forces conducted strikes against Dnipro City, Kryvyi Rih, and Zaporizhzhia City.[19]
- Russian occupation officials continued to forcibly transfer Ukrainian children from occupied territories in Luhansk Oblast to Russia under the guise that the children require special medical care.[20]
The Russian military clearly assesses that Ukrainian forces could cross the Dnipro River and conduct counter-offensive operations in eastern Kherson Oblast, possibly threatening all of the critical ground lines of communications (GLOCs) from Crimea to the mainland. Russian forces have been digging trench lines and concentration areas in eastern Kherson since early October 2022 in obvious preparation for the withdrawal from the west bank of the Dnipro River and Kherson City.[1] Russian troops are preparing either to defend in depth or to conduct operational or strategic delay operations. Russian forces clearly do not expect to be able to prevent Ukrainian forces from getting across the river, nor are the Russians prioritizing defensive positions to stop such a crossing. The Russian military is setting conditions for a protracted defense in eastern Kherson Oblast that could allow the establishment of a solid Ukrainian lodgment on the eastern bank of the Dnipro River. The assessment that follows examines the Russian defensive laydown and evaluates the expectations for the flow of operations likely guiding that laydown exclusively. This assessment makes no effort to determine whether Ukrainian forces intend to cross or are capable of crossing the Dnipro River in this region and offers no forecast about whether or not they will make any such attempt.
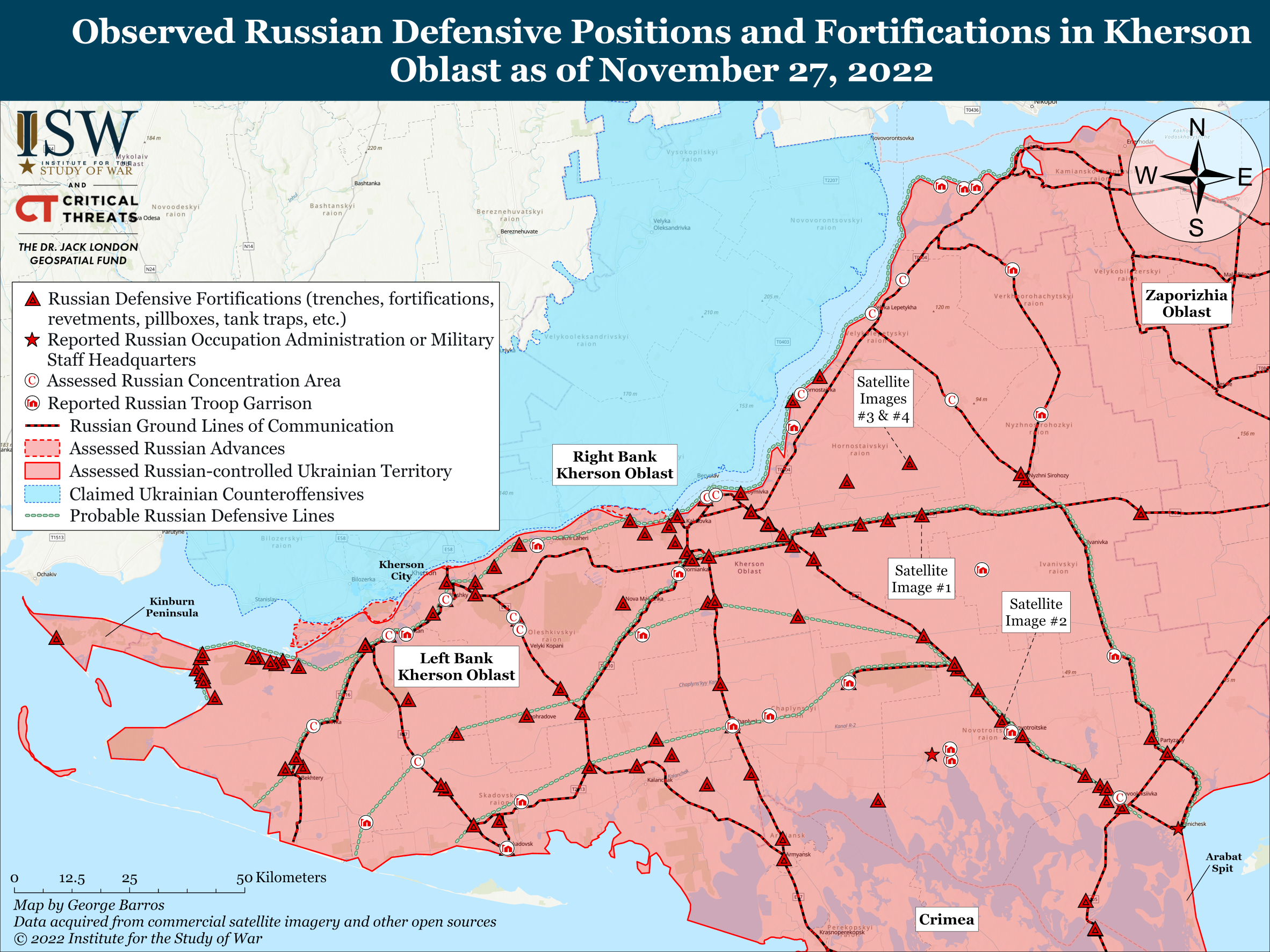
Russian forces are fortifying their positions along critical GLOCs in eastern Kherson Oblast against a possible future Ukrainian counteroffensive. Satellite imagery shows that Russian forces have prioritized digging trenches and erecting dragon’s teeth anti-tank defenses along GLOCs that connect Russian forces on the eastern (left) bank of the Dnipro River with southeastern rear areas in Kherson Oblast and Crimea as well as with eastern rear areas around Melitopol, Zaporizhia Oblast. Most of these field fortifications are situated directly on the GLOCs themselves and are primarily oriented perpendicular to the roads themselves. They are thus most like elaborate roadblocks rather than parts of cohesive defensive lines that stretch across multiple GLOCs and fields. Russian forces have also heavily fortified a 3km-wide strip of land separating the Kinburn Spit from mainland Kherson Oblast and along the beaches immediately south and east of the strip.

ISW Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, November, 24, 2024
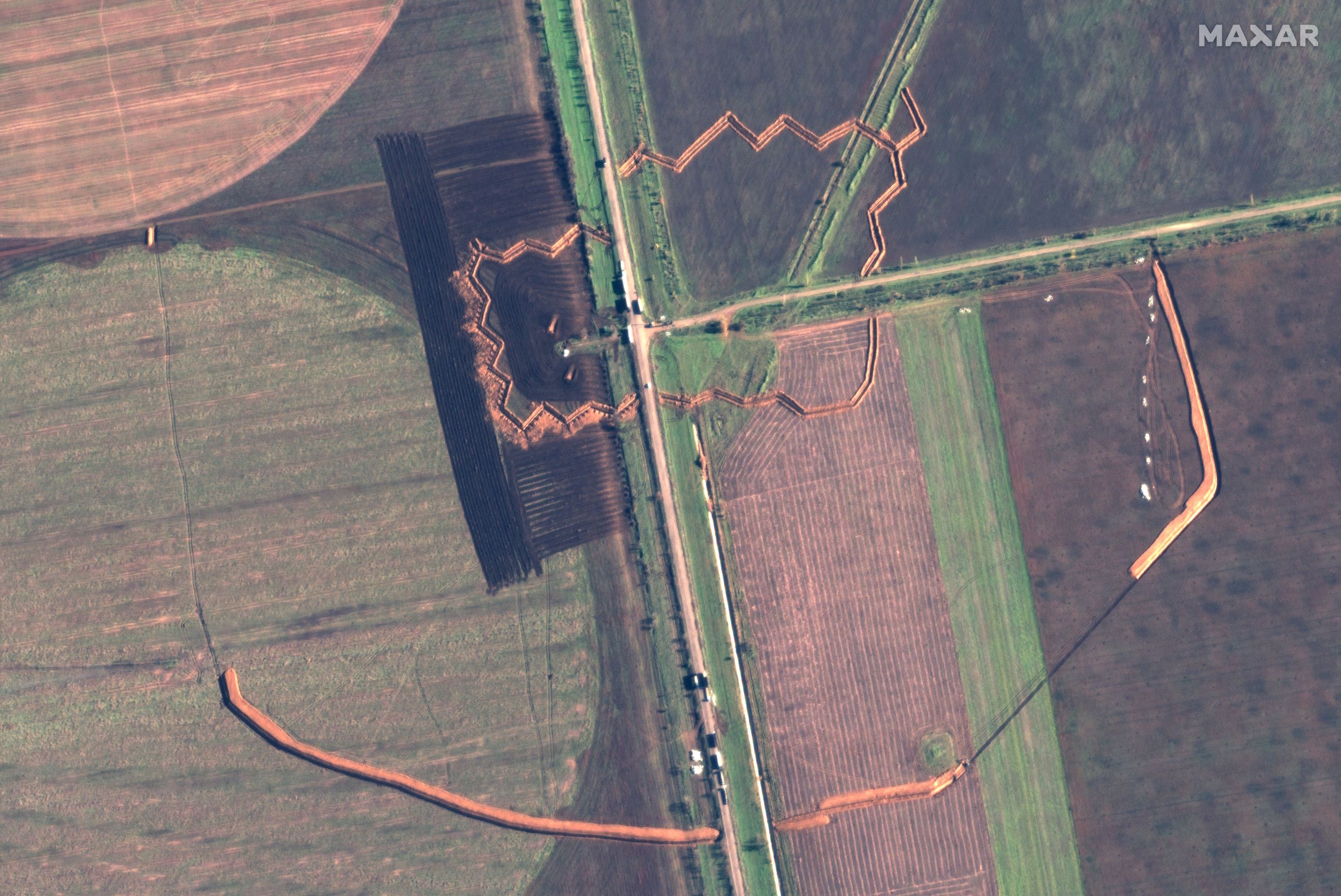

Trenches, fortifications, and tank obstacles near Stepne, Kherson Oblast, Russian-occupied Ukraine (15 NOV 2022) – Satellite image ©2022 Maxar Technologies
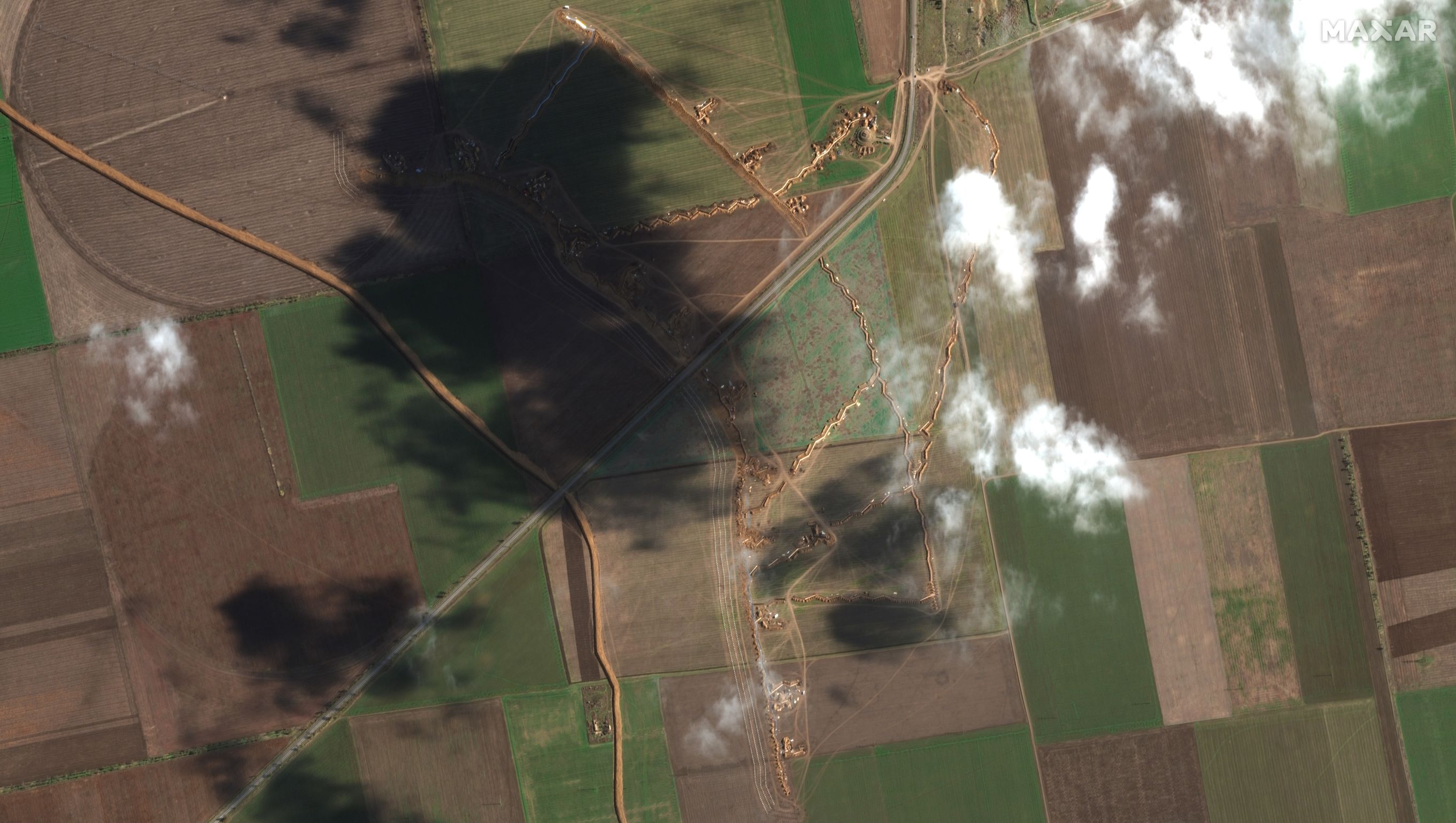

Trenches near Novotroitske, Kherson Oblast, Russian-occupied Ukraine (15 NOV 2022) – Satellite image ©2022 Maxar Technologies
The Russian defensive positions suggest that the Russian military leadership views the prospect of a Ukrainian counteroffensive across the Dnipro River as a serious threat. The array of Russian fortifications on and around the Kinburn Spit (as shown in the map) suggests that Russian forces do not expect to maintain positions on the spit itself if Ukrainian forces launch a counterattack against the spit; rather, Russian forces very likely expect Ukrainian forces to take the Kinburn Spit but intend to prevent them from advancing to mainland Kherson Oblast and to defend against an amphibious attack on the land immediately surrounding the spit’s connection to mainland Kherson Oblast.[2] The layered lines of defense (as shown in the map) provide Russian forces with multiple fallback positions if one defensive line happens to fall while the rest remain intact. Defenses near the spit suggest that Russian forces are concerned that Ukrainian forces could establish themselves on or near the spit and use that base to launch a drive from the west against their defensive positions that are otherwise generally oriented to defend against counter-offensive operations from the north.
Russian defensive positions are optimized to defend against Ukrainian forces attempting to advance along GLOCs rather than driving cross-country as Ukrainian forces have previously done. Russian forces concentrated most of their defenses at multiple locations astride critical GLOCs, establishing only a handful in the open fields between the highways. However, Ukrainian forces have previously conducted long cross-country drives in Kharkiv Oblast to capitalize on their success in breaking through Russian defensive lines near Balakliya, enabling them to more quickly advance on and surround Russian strongpoints such as Kupyansk and Izyum and push Russian forces from the Siverskyi Donets River in Kharkiv Oblast to the international border in most of the oblast.[3]
Most of the Russian field fortifications in eastern Kherson are nevertheless optimized to defend against drives along the roads and would be very vulnerable to envelopments across the open countryside. Many of the fortifications across the roads do not extend far past the roads themselves, often just far enough to provide good fields of fire from both sides onto the road itself. Most of these positions have open flanks terminating in the middle of fields. The flanks are often not refused (drawn back) or otherwise well-designed to deter or defend against attacks from the sides or rear. Many of these positions are not in tactical supporting distance of one another, moreover, which would make each vulnerable to Ukrainian tactical envelopments. Satellite imagery shows that Russian forces have constructed dragon’s teeth anti-tank structures around their positions immediately on the roads, but those anti-tank arrays do not extend far enough into the open fields to prevent Ukrainian tanks and other tracked vehicles from enveloping the Russian lines.
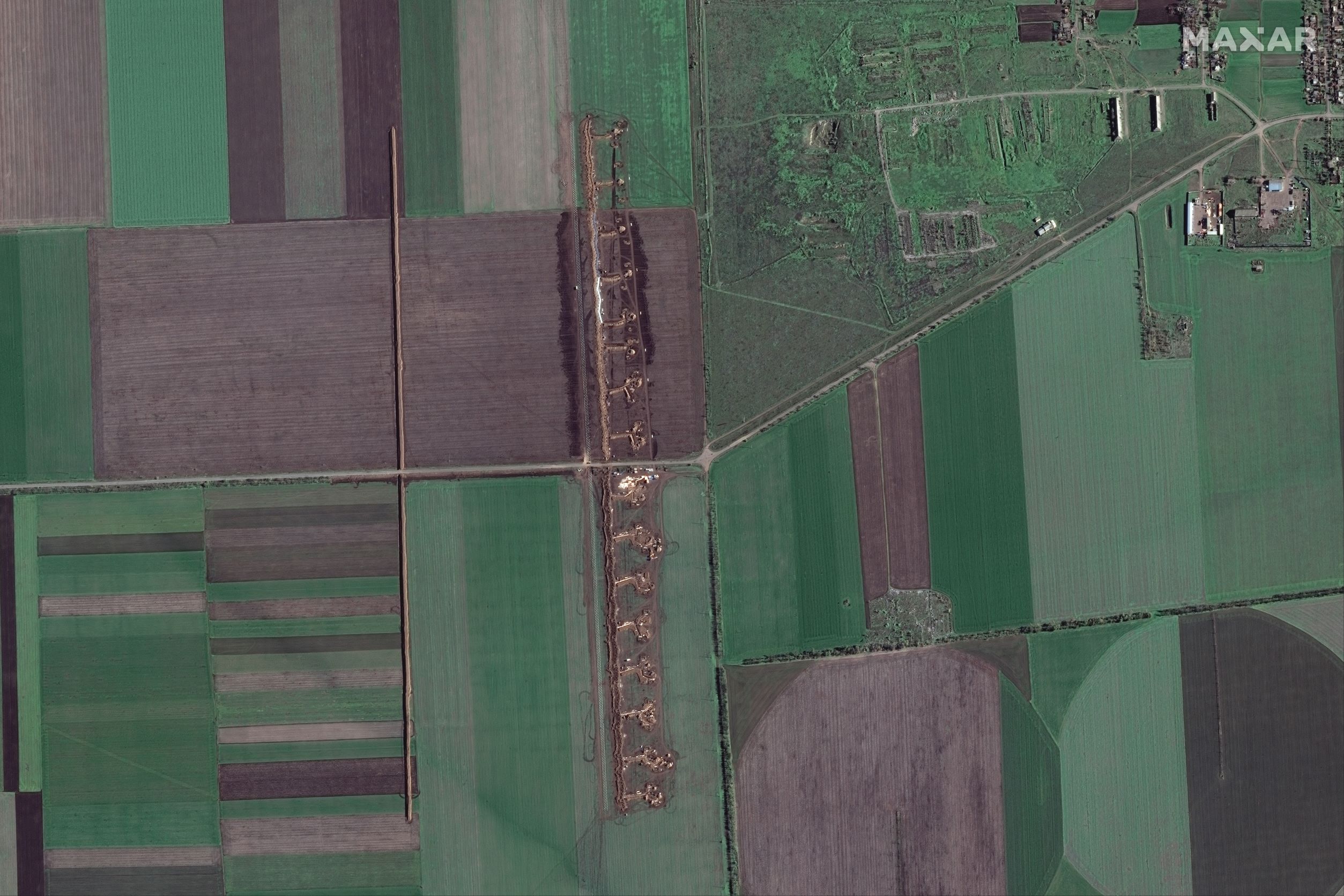

Trenches, fortifications, and tank obstacles near Velyka Blahovischenka, Kherson Oblast, Russian-occupied Ukraine (15 NOV 2022) – Satellite image ©2022 Maxar Technologies
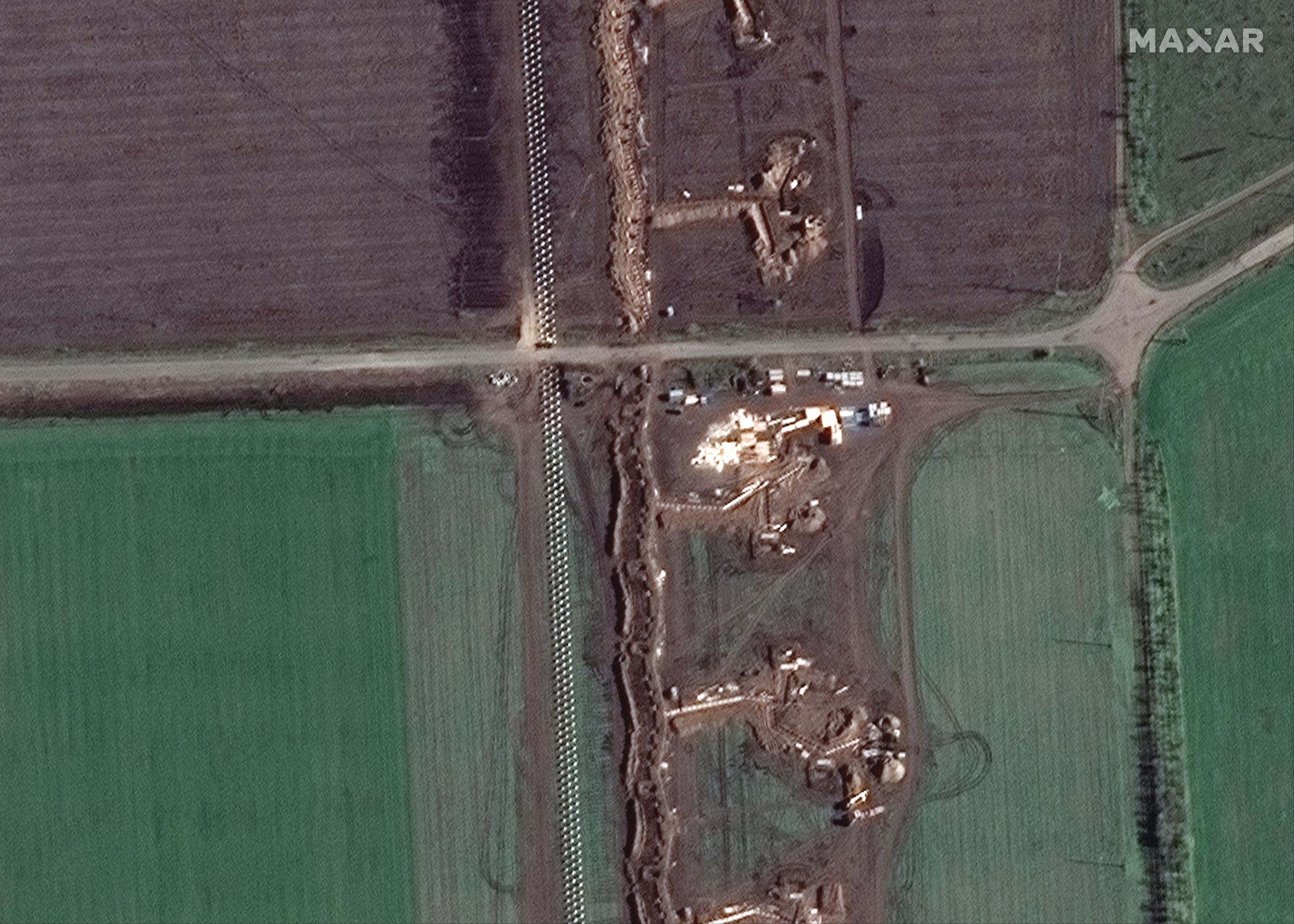

Trenches, fortifications, and tank obstacles near Velyka Blahovischenka, Kherson Oblast, Russian-occupied Ukraine (15 NOV 2022) – Satellite image ©2022 Maxar Technologies
The tactical vulnerabilities of these defensive positions are mirrored in a similar operational-level vulnerability. Russian forces would be under threat of attacks on their uncovered flanks or even complete encirclement if Ukrainian forces were able to cross the Dnipro River both in the Kherson City-Nova Kakhovka area to the north of most Russian fortifications and to initiate a substantial mechanized campaign from a base on or near the Kinburn Spit to the west of most fortifications.
Russian forces may be attempting to delay (slow down) rather than defend against (stop) a Ukrainian offensive on the east (left) bank of the Dnipro River. Russian forces would presumably delay until they can deploy more reinforcements to either stop or slow Ukrainian forces from breaking through secondary and tertiary lines of defense that protect critical GLOCs both to Crimea and to western Zaporizhia Oblast (as shown in the map). It is unclear if the Russian military leadership foresees a delay mission at the operational or the strategic level. An operational-level delay would require holding long enough to allow forces already in theater to move from other areas to eastern Kherson. A strategic-level delay would mean holding long enough to allow newly-mobilized units time to arrive in theater. The difference lies primarily in the Russian military’s perception of time-space relationships in this area. Russian forces would likely take many months to drive through a Ukrainian defensive array if the Ukrainians had built one like the one described in this report. If Russian forces expect Ukrainian forces to take months to break through their defenses in this region, they could reasonably expect additional mobilized forces or partially-trained conscripts to arrive in time to stop and possibly reverse the Ukrainian counter-offensive.
But Ukrainian counter-offensives have sometimes moved much more rapidly than that, once launched. If Ukrainian forces were able to penetrate several of the Russian defensive lines in Kherson Oblast in weeks rather than months, then Russian forces would have to reinforce from other parts of the theater with forces already deployed and operating there. The defensive array itself offers no insight into the Russians’ expectations in this regard.
Russian forces have likely deployed mobilized personnel to the primary lines of defense and pulled experienced, professional units to the secondary and tertiary lines of defense, a deployment pattern that could lead to more rapid Ukrainian advances.[4] As ISW has previously reported, Russian mobilized personnel are generally poorly trained, equipped, and led, significantly increasing casualties among mobilized personnel and decreasing their willingness to fight.[5] Such reports are so frequent and pervasive that they have divided the Russian information space and prompted swift punishment and suppression.[6] Manning Russian frontline fortifications with these less effective, less organized, and poorly equipped and supplied personnel could lead to them collapsing or falling back faster than Russian military leadership may have planned, potentially disrupting Russian time-space relationship expectations.
The Russian effort to prepare extensive defensive positions in eastern Kherson, however well or poorly executed, highlights the critical importance this terrain holds for the future course of the war. The GLOCs that Russian forces seek to defend in Kherson Oblast include almost all remaining routes essential to maintaining military operations across southern Ukraine, including the two main highways connecting mainland southern Ukraine to Crimea. Losing even one of these GLOCs would likely strain Russian logistics supporting operations in eastern Kherson Oblast and western Zaporizhia Oblast and could allow Ukrainian forces to advance close enough to the remaining highway to interdict it. As ISW has previously reported, Russian forces may seek to use the Arabat Spit as a third GLOC between Crimea and southern Ukraine that Ukrainian forces could threaten by targeting one of the two bridges essential to maintaining the GLOC.[7] The Russian failure to hold these GLOCs would force the Russians to rely entirely on the GLOC from Rostov through Mariupol and Melitopol, itself under threat of a Ukrainian counter-offensive from the north. If Ukrainian forces established themselves in eastern Kherson Oblast, they could threaten an additional counter-offensive toward Melitopol from the west, which Russian forces would likely struggle to defend against.
Elements of the Russian information space are beginning to lose faith in Russian forces’ ability to hold key areas in western Zaporizhia Oblast, possibly setting long-term information conditions for a Russian withdrawal from this area. Russian milbloggers have made recent claims that Ukrainian forces are preparing to retake the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (ZNPP) in Enerhodar.[8] Recent Russian-language discourse on Twitter references such posts to claim that Russian milblogger channels, especially those affiliated with Wagner Group, are promulgating a narrative that Russian forces are preparing to leave the ZNPP soon.[9] The head of the Ukrainian nuclear energy agency Energoatom stated on November 26 that Russian forces may be preparing to leave the ZNPP and that the first indication of these preparations is unspecified “Russian publications”—possibly referring to social media discourse—that suggest Russia should transfer control of the ZNPP to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).[10] Though ISW has seen no evidence of an imminent Ukrainian counteroffensive in Zaporizhia Oblast that could threaten Russian positions in Enerhodar or Melitopol, this discourse combined with the consistent thread of Russian milblogger, occupation officials, and state media claims of a Ukrainian force concentration along this axis to threaten Melitopol may also prepare the information space for an eventual Russian withdrawal regardless of whether such claims actually intend to do so.[11] Frequent Russian official claims that Ukrainian forces continue to shell the ZNPP could also intentionally or unintentionally support this condition-setting.[12]
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter