Key Takeaways
- Russian forces are likely using Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) in Enerhodar to play on Western fears of a nuclear disaster in Ukraine, attempting to thereby degrade the will of Western powers to provide military support to a Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Russian forces likely set fire to the prison complex holding Ukrainian POWs in occupied Donetsk Oblast but blamed Ukraine for an alleged precision strike using Western-supplied military equipment, likely to increase US hesitancy to continue providing HIMARS to Ukraine.
- Moscow is likely continuing efforts to leverage its relationship with Tehran in order to secure drones for use in Ukraine.
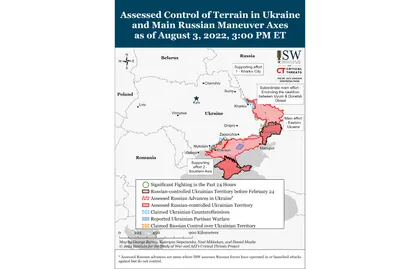
- Russian forces conducted a limited ground attack northwest of Slovyansk and continued efforts to advance on Bakhmut from the northeast, east, and southeast.
- Russian forces are prioritizing frontal assaults on Avdiivka and failed to gain ground in Pisky.
- Russian forces are reportedly forming a strike group to prevent Ukrainian counteroffensives in northern Kherson Oblast or counterattack against them.
- Russian occupation authorities may allow both in-person and online voting in upcoming pseudo-referenda on the annexation of occupied Ukrainian territory into Russia, enabling more straightforward Russian vote rigging.
Russian forces are likely using Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) in Enerhodar to play on Western fears of a nuclear disaster in Ukraine, likely in an effort to degrade Western will to provide military support to a Ukrainian counteroffensive. International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Director General Rafael Grossi said on August 3 that Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (NPP), which is currently occupied by Russian forces, is “completely out of control” and that “every principle of nuclear safety has been violated” at the plant.[1] He warned that Russian forces are not respecting the physical integrity of the plant and pleaded with Russia and Ukraine to quickly facilitate a visit of IAEA monitors to the complex. Russian Zaporizhia Occupation Administration Head Evgeniy Balitskyi responded that the IAEA was welcome at the plant: “We are ready to show how the Russian military guards it today, and how Ukraine, which receives weapons from the West, uses these weapons, including drones, to attack the nuclear plant, acting like a monkey with a grenade.”[2] Russian officials are framing Ukraine as irresponsibly using Western-provided weapons and risking nuclear disaster to dissuade Western and other allied states from providing additional military support to Ukraine’s looming southern counteroffensive.
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
Follow our coverage of the war on the @Kyivpost_official.
Russian forces based around the NPP have attacked Ukrainian positions in Nikopol and elsewhere in recent weeks, intentionally putting Ukraine in a difficult position—either Ukraine returns fire, risking international condemnation and a nuclear incident (which Ukrainian forces are unlikely to do), or Ukrainian forces allow Russian forces to continue firing on Ukrainian positions from an effective “safe zone.” Ukrainian Mayor of Enerhodar Dmytro Orlov reported on August 3 that Russian forces launched rockets on Enerhodar from neighboring villages to falsely accuse Ukrainian forces of shelling Enerhodar and endangering the NPP.[3] ISW assessed on July 21 that Russian forces may be storing heavy military equipment in the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) in Enerhodar to protect it from Ukrainian strikes.[4] Russian forces have also likely staged false flag attacks around Enerhodar since early July, as ISW previously reported.[5]

N. Korean Troops Massed in Russia to Enter Ukraine War ’Soon’: Pentagon Chief
Russian forces likely set fire to the prison complex holding Ukrainian POWs in occupied Donetsk Oblast but blamed Ukraine for an alleged precision strike using Western-supplied military equipment, likely to deter additional Western military support to Ukraine. The Ukrainian Main Military Intelligence Directorate (GUR) reported that it has determined that the Wagner Group deliberately set fire to the prison complex on July 28. This report is consistent with the damage observable in Russian-provided video of the site. The GUR reported that Wagner forces “mined” the building with unspecified flammable substances, which led to a rapid spread of fire throughout the building.[6] Russian-provided footage and commercial satellite imagery from the colony showed that the walls of the building were burned but still standing and did not reveal shell craters or other indicators consistent with an artillery strike. ISW previously reported that imagery from the site shows that the attack only damaged one building, did not collapse the walls of that building, and did not leave any shell craters in the vicinity, very strongly suggesting that the destruction of the prison was the result of either a precision strike or an internally planted incendiary or explosive.[7] Russian officials previously claimed that the deaths of the POWs were the result of a Ukrainian HIMARS strike, likely as a component of the ongoing Russian information operation attempting to dissuade the US from continuing to provide Ukraine with HIMARS.
The Kremlin is likely continuing efforts to leverage its relationship with Tehran in order to receive drones for use in Ukraine. Russian state-owned space agency Roscosmos announced on August 3 that Russia will launch a remote-sensing satellite (named “Khayyam”) into orbit on behalf of Iran on August 9.[8] The Kremlin may intend this launch to encourage or repay Tehran for the provision of Iranian drones that would be employed in operations in Ukraine, and possibly other military equipment or support. Iran has a huge ballistic missile arsenal and domestic missile manufacturing capabilities that it could provide to Russia in exchange for economic and military cooperation.[9] Iran has prioritized the development of its military space program in recent years and launched one satellite in April 2020 and one in April 2022. US and Middle Eastern officials stated as early as June 2021 that Russian officials were preparing to send a Russian-made Kanopus-V satellites to Iran, which would expand Tehran’s overall surveillance capabilities in the Middle East and beyond.[10] As ISW reported on August 2, Russian and Iran are likely continuing to facilitate cooperation through recently signed bilateral aviation agreements in order to bolster Russian military capabilities in Ukraine and assist Tehran with sanctions mitigation.[11]
The Russian Defense Ministry has altered the focus of its reporting after the fall of Lysychansk, likely to orient on narratives that resonate positively with milbloggers and war correspondents rather than those that draw criticism from that community. The Russian Defense Ministry has shifted its reporting style to focus on claims of declining Ukrainian morale and successful Russian strikes on Western-provided military equipment, rather than reporting on day-to-day Russian advances on the frontline.[12] Russian forces have made limited gains around Bakhmut and Avdiivka in recent days, but the Russian Defense Ministry has not claimed territorial gains around the theater since at least the fall of Lysychansk. Milbloggers, war correspondents, and other groups have criticized the Defense Ministry and the Kremlin for exaggerated and inaccurate claims of territorial gains, undermining Moscow’s narratives and credibility.[13] The Defense Ministry apparently flirted with the idea of suppressing or attempting to control the milblogger community, but it seems instead to have opted to adjust its own narratives.[14] The Defense Ministry is now letting milbloggers, war correspondents, and DNR officials cover the situation unfolding in Avdiivka, Pisky, and south of Bakhmut positively without making claims of its own that might draw criticism. Milbloggers released footage from the reported capture of the Butivka Coal Mine ventilation shaft and on the southern outskirts of Pisky, where they celebrated recapturing small segments of years-long contested territory–but the Defense Ministry has made no statement on the subject.[15] Some of the milbloggers such as Maksim Fomin (known under alias Vladelen Tatarzkiy) have previously served within DNR units and include anecdotes about their service in the Donetsk City area prior to Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine. Such coverage of the war likely aims to boost morale among DNR and Russian fighters. The Kremlin or the Defense Ministry may have decided that the milbloggers and war correspondents are more credible sources for the constituencies it cares most about and realized that its own claims were losing credibility. They may alternatively be focusing on narratives that generate positive resonance within that community.
Authors: Kateryna Stepanenko, Katherine Lawlor, Karolina Hird, Angela Howard, and Frederick W. Kagan
See the full report here.
You can also highlight the text and press Ctrl + Enter